The Fourth Industrial Revolution
Discover the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) – a transformative era of advanced technologies like AI, IoT, blockchain, and robotics, redefining industries and societies. Uncover its impact on jobs, daily life, and the economy, while exploring the need for ethical considerations and human-centric approaches to embrace the future responsibly.”
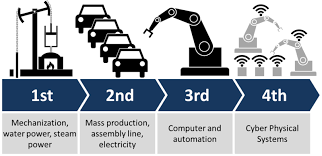
The world has witnessed several significant transformations over the centuries, each marked by pivotal technological advancements that shaped human progress. From the steam engine and electricity to the internet and smartphones, these innovations have profoundly impacted the way we live and work. Today, we stand on the brink of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, a new era characterized by a fusion of physical, digital, and biological technologies that is redefining our understanding of society, economy, and human potential.

The Fourth Industrial Revolution Defined:
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, often abbreviated as 4IR or Industry 4.0, represents a remarkable convergence of cutting-edge technologies that blur the lines between the physical, digital, and biological domains. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, robotics, 3D printing, nanotechnology, and biotechnology are at the core of this revolution. The integration and interplay of these technologies are unlocking unprecedented opportunities for innovation and disruption across industries.
Key Technological Pillars:
a. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and making autonomous decisions. This technology empowers automation, personalization, and predictive analytics in various sectors, revolutionizing how businesses operate and how individuals interact with technology.
b. Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices and objects that can collect, exchange, and act upon data without human intervention. This interconnectedness paves the way for smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and a plethora of applications that enhance efficiency and convenience in our daily lives.
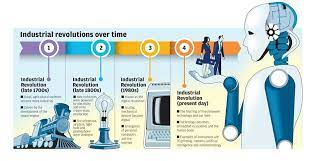
c. Blockchain: Blockchain, a decentralized and secure digital ledger, has disrupted industries like finance, supply chain, and healthcare. Its tamper-resistant nature, transparency, and trustless transactions offer immense potential for streamlining processes and eliminating intermediaries.
d. Robotics and Automation: Advancements in robotics are ushering in a new era of automation, transforming manufacturing, agriculture, healthcare, and logistics. Robots are becoming more sophisticated, collaborating with humans, and taking on repetitive or dangerous tasks, leading to increased productivity and improved safety.
Impacts on Society and the Economy:
a. Employment and Workforce Shifts: The Fourth Industrial Revolution brings both excitement and concerns about job displacement. While automation may replace some jobs, it will also create new ones, demanding skills in areas like AI programming, data analysis, cybersecurity, and human-machine interaction.
b. Education and Skills Development: To harness the opportunities presented by 4IR, educational systems must adapt and prioritize skills relevant to the digital age. A focus on critical thinking, creativity, problem-solving, and adaptability will be essential to equip individuals for the workforce of the future.
c. Economic Transformation: Industry 4.0 has the potential to revolutionize economies worldwide. Countries embracing and investing in emerging technologies are likely to gain a competitive edge and experience significant economic growth.
Ethical and Societal Considerations:
As technology permeates every aspect of life, ethical considerations become paramount. Issues related to data privacy, algorithm bias, security, and AI ethics need careful attention to ensure a fair, inclusive, and responsible technological future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR)?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, also known as 4IR or Industry 4.0, refers to a transformative era characterized by the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, blockchain, and biotechnology. It marks a convergence of the physical, digital, and biological worlds, reshaping industries and societies.
What are the key technologies driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Some of the key technologies driving 4IR include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Blockchain
- Robotics and Automation
- 3D Printing
- Nanotechnology
- Biotechnology
How will the Fourth Industrial Revolution impact our daily lives?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is set to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. It will bring greater automation, personalized services, and more efficient processes. Smart homes, autonomous vehicles, personalized healthcare, and smart cities are just a few examples of the potential changes that may enhance our daily experiences.
What are the implications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution on jobs and employment?
4IR will lead to job displacement in some areas, particularly in industries that can be easily automated. However, it will also create new job opportunities in emerging fields like AI programming, data analysis, cybersecurity, and human-machine interaction. Upskilling and reskilling the workforce will be crucial to adapt to the changing job landscape.
How can businesses leverage the Fourth Industrial Revolution for growth?
Businesses can harness 4IR technologies to improve efficiency, streamline operations, and enhance customer experiences. Adopting AI-driven analytics, implementing IoT-based systems, and exploring blockchain applications are some ways businesses can stay competitive and drive growth.
What role will education play in preparing for the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Education will play a pivotal role in preparing individuals for the future workforce. Fostering skills such as critical thinking, creativity, problem-solving, adaptability, and digital literacy will be essential to thrive in the 4IR era.
What are the potential risks associated with the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
As with any major technological shift, 4IR comes with risks and challenges. Concerns include data privacy and security, algorithm bias, job displacement, and ethical considerations related to AI and automation. Addressing these issues will be crucial to ensure a responsible and inclusive technological future.
How will the Fourth Industrial Revolution impact developing countries?
Developing countries have the opportunity to leapfrog traditional stages of development by embracing 4IR technologies. Strategic investments in infrastructure, digital connectivity, and skill development can help these countries bridge the technological divide and accelerate economic growth.
How can society ensure a human-centric approach during the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Maintaining a human-centric approach involves prioritizing the ethical use of technology, safeguarding individual privacy, and ensuring technology benefits all segments of society. Collaboration among governments, businesses, academia, and civil society is essential to shape policies and frameworks that prioritize human well-being.
What can individuals do to adapt to the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Individuals can prepare for the Fourth Industrial Revolution by embracing lifelong learning, upskilling in emerging technologies, and developing a growth mindset. Staying curious, adaptable, and open to new opportunities will be crucial in navigating the changing landscape of the 4IR.
TO CLICK DAILY NEWSPAPER PDF LINK
TO SEE RESEARCH INFORMATION
TO MORE UPDATE FOLLOW US
Conclusion:
The Fourth Industrial Revolution presents an unprecedented wave of opportunities and challenges. Embracing these advancements responsibly can lead us towards a future of unimaginable possibilities. However, it will require collaborative efforts from governments, businesses, academia, and society to ensure that the benefits of 4IR are shared equitably, and the potential risks are mitigated. As we stand on the cusp of this technological leap into the future, let us navigate this revolution with wisdom, empathy, and a human-centric approach.
